Understanding the Difference Between Bhang and Ganja: A Complete Guide

Cannabis has been a part of Indian culture for centuries, woven into religious, social, and medicinal practices. However, when it comes to the difference between bhang and ganja, many people get confused. While both come from the cannabis plant, their uses, effects, legal status, and cultural significance vary significantly. Understanding these differences is essential, especially given the rising concerns about substance use and the growing demand for drug addiction treatment in India.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the difference between bhang and ganja, comparing their origins, consumption methods, effects on the body and mind, and the societal impact they have. This will help clear up any confusion and provide you with a more comprehensive understanding of these two forms of cannabis.
What Is Bhang?
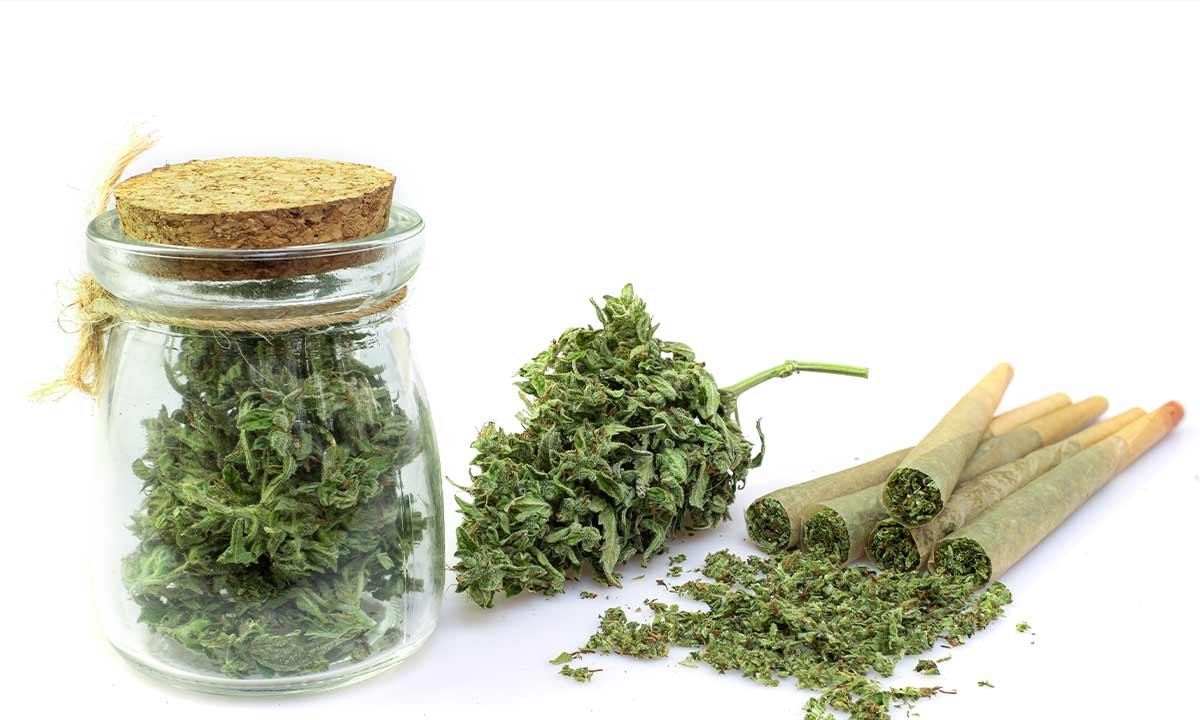
Bhang is a traditional Indian preparation made from the leaves and seeds of the cannabis plant. Unlike ganja, which comes from the buds of the plant, bhang is a much milder form of cannabis. It's commonly used in various food and drink preparations, such as the popular bhang lassi (a cannabis-infused yogurt drink) and bhang goli (small edible balls).
Cultural Significance of Bhang
Bhang holds immense cultural importance, particularly during festivals such as Holi and Shivaratri. It is closely tied to the worship of Lord Shiva, who is said to consume bhang as part of his spiritual rituals. During these festivals, bhang is consumed by devotees and revelers to enhance their experience and foster a sense of togetherness and spirituality.
Legal Context in India
The difference between bhang and ganja becomes especially evident when examining their legal standing. Bhang is culturally accepted and often legally sold during festivals like Holi. Its consumption is permitted in some states, but it is regulated to ensure that it doesn’t cause harm or misuse. In contrast, ganja remains highly controlled due to its higher THC content.
People facing legal and health complications due to ganja consumption often seek help from a nasha mukti kendra in Delhi or other drug de-addiction centers.
What Is Ganja?
Ganja refers to the dried flowering buds of the cannabis plant, which contain high levels of THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the compound responsible for the "high" that users experience. Ganja is typically smoked, vaporized, or used in edibles, offering a stronger, more immediate effect than bhang.
Common Use and Consumption
Ganja is most commonly smoked, either in joints or pipes, or vaporized for quicker effects. It has gained popularity as a recreational drug, but it is also used medicinally, especially in managing chronic pain, anxiety, and other mental health conditions like panic disorder and depression. It is important to note that ganja is more potent than bhang and its effects are much faster.
Legal Status in India
The difference between bhang and ganja is stark when it comes to their legal status. While bhang is consumed openly during certain festivals, ganja is illegal in most contexts. Under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, ganja is prohibited, except for limited medicinal use. This legal difference is crucial in understanding the societal implications of both forms of cannabis in India.
Bhang vs. Ganja: A Quick Comparison
|
Aspect |
Bhang |
Ganja |
|
Source |
Leaves & seeds of cannabis |
Flowering buds of cannabis |
|
Potency |
Low to moderate THC |
High THC |
|
Method of Use |
Ingested (drink, edible) |
Smoked/vaporized |
|
Legal Status |
Permitted during festivals |
Illegal (except medicinal use) |
|
Cultural Link |
Religious, ceremonial |
Spiritual ascetics, recreational |
How Bhang and Ganja Affect the Mind and Body
Both bhang and ganja impact the body and mind due to the cannabinoids they contain, but their effects differ greatly.
Bhang
- Onset Time: The effects of bhang take much longer to be felt, often taking 2-3 hours for full onset.
- Psychological Effects: Bhang is typically associated with mild relaxation, euphoria, and a distorted sense of time and space. The effects are relatively gentle compared to ganja.
- Physiological Effects: Bhang is known to aid digestion and reduce stress. It is also used as a mild sedative in some cultures.
Ganja
- Onset Time: Ganja acts quickly when smoked or vaporized, with effects typically taking 30 minutes or less to kick in.
- Psychological Effects: Ganja is much stronger, often producing a sense of euphoria, heightened awareness, and altered perception. However, it can also lead to anxiety or paranoia in some individuals, especially when consumed in large quantities.
- Physiological Effects: Ganja can increase heart rate, cause dry mouth, and impair coordination. Long-term use may lead to dependence, memory issues, and other cognitive effects.
Medicinal Uses and Health Risks
The difference between bhang and ganja also extends to their medicinal applications and associated risks.
Ganja
- Medicinal Uses: Ganja is widely used for pain management, treating nausea (particularly for chemotherapy patients), and alleviating anxiety and insomnia.
- Health Risks: Despite its medicinal benefits, ganja carries risks, including the potential for addiction, respiratory problems (if smoked), and mental health issues, such as paranoia and psychosis in susceptible individuals.
Bhang
- Medicinal Uses: Bhang is generally considered to have milder medicinal properties, used for stress relief, digestive issues, and general wellness.
- Health Risks: While bhang is safer than ganja, overconsumption can still lead to nausea, dizziness, or mild hallucinations. It can also become addictive if consumed frequently.
Cultural and Legal Implications in India
The difference between bhang and ganja has major cultural and legal implications in India.
Bhang
Bhang is deeply embedded in Indian culture, particularly during religious festivals. It is often seen as a sacramental substance, with few negative connotations. However, as cannabis becomes a topic of modern-day debate, the line between cultural use and potential misuse is becoming blurry.
Ganja
The use of ganja is illegal in most parts of India, leading to legal battles and concerns about its misuse, especially among youth. However, there are growing calls for the decriminalization of cannabis for medicinal use, as more research supports its therapeutic properties.
Why the Difference Between Bhang and Ganja Matters Today
The difference between bhang and ganja is crucial in the context of public health and policy. With the increasing misuse of cannabis, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the distinct roles that bhang and ganja play in Indian society. As attitudes toward cannabis evolve, recognizing the difference between the two is key to addressing health concerns, legal challenges, and cultural perceptions.
Find Support With Athena Behavioral Health
If you or someone you know is struggling with cannabis misuse—whether it’s the recreational use of ganja or the cultural consumption of bhang—Athena Behavioral Health is here to help. We provide compassionate, clinical support for addiction and mental health challenges, offering personalized programs designed to aid in recovery.
Conclusion
To recap, the difference between bhang and ganja is rooted in their origin, potency, use, and legal status. While bhang remains culturally significant and is legally accepted during certain festivals, ganja is often associated with recreational use and is subject to stricter legal controls. Understanding these distinctions is essential not only for cultural appreciation but also for responsible consumption and awareness of the health risks involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
The primary difference between bhang and ganja lies in their source and potency. Bhang is made from the leaves and seeds of the cannabis plant and has low to moderate THC, while ganja is made from the flowering buds of the plant and has high THC.
Yes, bhang is legally consumed during festivals like Holi and Shivaratri in some states of India. However, it is regulated and only available in specific circumstances.
Ganja is illegal in most parts of India except for specific medicinal uses. Some states have legalized its use for medical purposes, but it requires a prescription.
Bhang has a slower onset and milder effects compared to ganja. Ganja acts quickly and can produce stronger psychological effects such as euphoria and altered perception.
Due to its high THC content, ganja can have more potent and potentially harmful effects, including dependency and mental health issues. Bhang is generally considered safer but can still cause mild side effects when consumed in excess.
Bhang is consumed during religious festivals, particularly Holi and Shivaratri, where it is believed to bring blessings and enhance spiritual experiences.
While bhang is less likely to cause addiction than ganja, it can still lead to dependence if consumed frequently, especially in cultural contexts.
If you or someone you know is struggling with cannabis misuse or addiction, consider seeking help from a professional treatment center like Athena Behavioral Health for personalized care and support.